What is Known About Urea Control in UPW Systems?
Date Published 2022 | Conference materials
To access our resources you will need to be a member of UltraFacility, log in to your account or purchase a membership to view this content.
Urea is chemical widely used as nitrogen fertilizer and feed supplement. It is nonvolatile, difficult to oxidize, non-ionic, and highly soluble in water and has a low molecular weight (60 g/mol). Conventional ultrapure water purification techniques are not able to remove it from UPW, and it is a common contaminant in every water reclaim system. Urea naturally decomposes into ammonia, that even at part per billion concentrations, may negatively impact the performance of the acid-catalyzed, chemically amplified photoresists used in today’s DUV photolithography processes. Due to the increasing demand for high quality UPW in the semiconductor industry with tight specs and need to promote water conservation, it is important to treat urea in UPW
Related content
Can advanced oxidation technology help control TOC in semiconductor water?
End-of-Pipe Semiconductor Wastewater Reclaim
U-PURTM – A Metal-Free Combination of Several UPW Polishing Steps in a Multifunctional Reactor for the Removal of TOC and H2O2 Traces
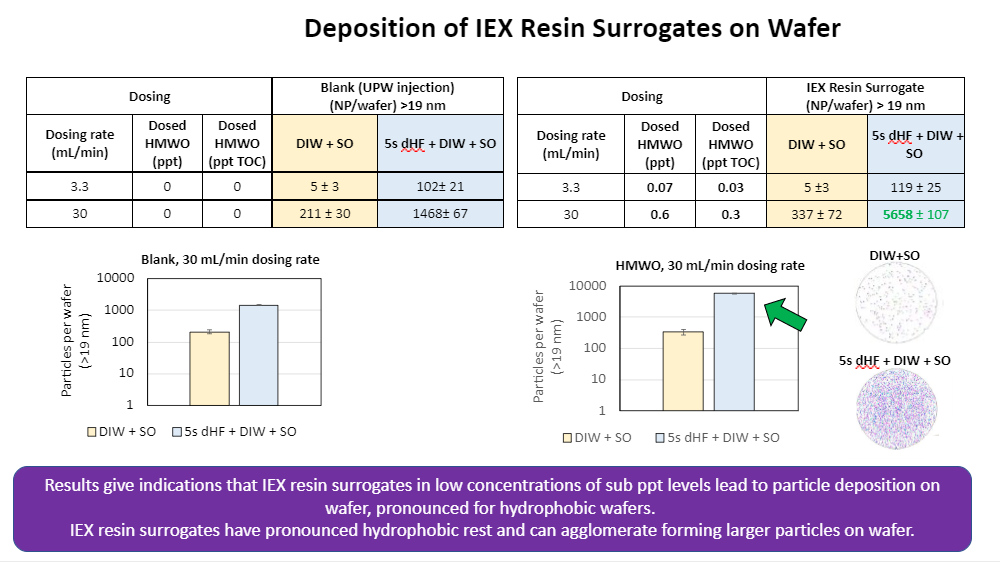
Establishing Correlations between UPW Quality and Particle Deposition on Silicon 300 mm Wafer
Back to results